How often should you have an eye check-up?
10/07/2025
22/11/2024
Osmolarity refers to the concentration of solutes in tears, and its measurement provides valuable insights into the stability and quality of the tear film, enabling more personalized and effective treatment for each patient.
An increase in tear osmolarity is a key indicator of tear dysfunction and is associated with various forms of dry eye.
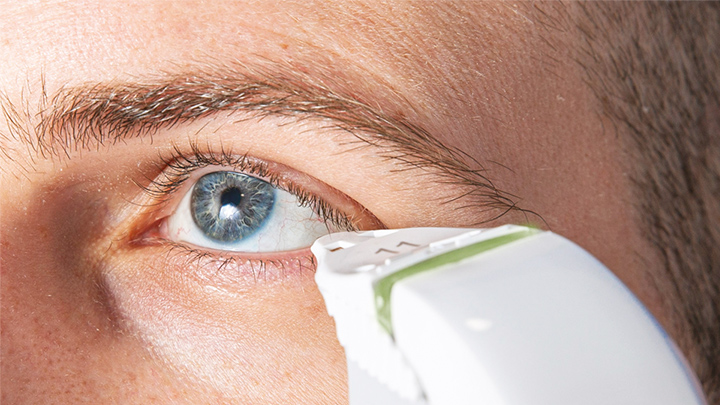
This non-invasive and rapid test requires no prior preparation from the patient and takes only a few minutes to perform. A small collection device is gently placed on the lower eyelid margin to absorb a tiny amount of tear. The tear sample is then analyzed using an osmolarity analyzer, which measures the solute concentration in the tear film. The device provides a numerical reading of osmolarity in milliosmoles per litre (mOsm/L). Osmolarity values greater than 308 mOsm/L or a difference of more than 8 mOsm/L between the two eyes indicate significant tear film dysfunction.
The test is recommended for patients exhibiting symptoms of dry eye, such as:
The osmolarity test is primarily used for the diagnosis and monitoring of the following conditions:
Dry eye syndrome: A common condition characterized by reduced tear production or excessive tear evaporation, resulting in elevated osmolarity.
Meibomian gland dysfunction: A disorder affecting tear quality, which can contribute to abnormal osmolarity.
Blepharitis: Inflammation of the eyelids that disrupts the composition of the tear film.
Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as Sjögren's syndrome that reduce tear production and increase osmolarity.
Joaquim Fernández and Antonio Beltrán, Department of Ocular Biometry and Physiology
El ojo seco es una patología crónica que consiste en la escasez de la cantidad de lágrima y/o en el deterioro de la calidad de la misma produciendo una inflamación de la superficie del ojo. Las lágrimas son esenciales para mantener la superficie del ojo lubricada, proporcionarle nutrientes y protegerlo contra infecciones. En este capítulo hablamos con el doctor Rubén Delgado sobre algunas cuestiones básicas sobre el ojo seco y los tratamientos que ofrecemos en Barraquer.